The Role of Ethernet Switching in Modern Networks
Ethernet switching is crucial in modern networks, enabling efficient data transfer and connectivity. It manages traffic by directing data packets between devices, ensuring fast, reliable communication. This technology supports scalable, high-performance networks essential for businesses, facilitating seamless integration of various applications and devices while maintaining network stability and security.
Introduction to Ethernet Switching
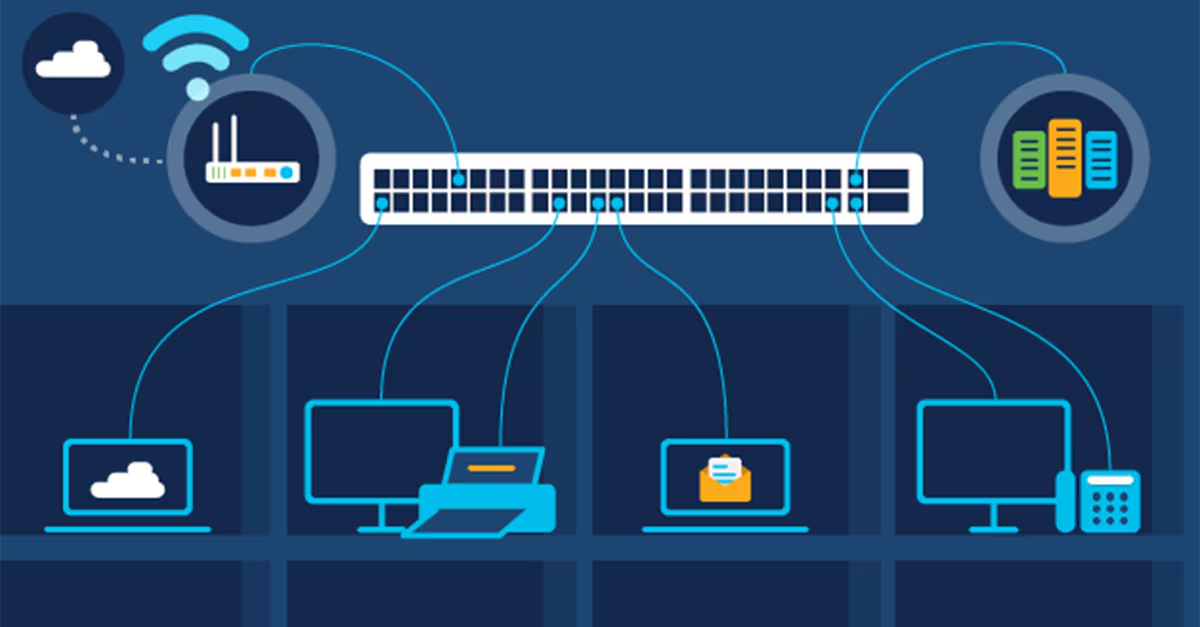
Ethernet switching is a cornerstone in the architecture of modern digital networks, facilitating seamless communication between multiple devices. Unlike simpler network devices such as hubs, an ethernet switch intelligently directs data to its intended destination, significantly improving network efficiency. This functionality is crucial for ensuring networks operate smoothly and without unnecessary congestion. Ethernet switches help maintain robust and efficient connectivity in enterprise settings or home networks.
Ethernet switches’ thoughtfully designed routing decisions mean that data packets are only sent to the devices that need them, thereby optimizing network performance and reducing the burden on network bandwidth. In a world where digital transformations are at their peak, having a reliable switch to manage data traffic efficiently is indispensable for both productivity and security.
How Ethernet Switches Work
Switches operate by receiving incoming data packets and determining their destination addresses. They then forward these packets to the correct devices, whether computers, servers, or other connected gadgets. This selective forwarding reduces unnecessary network traffic and enhances overall network performance. Switches keep an internal table that matches MAC addresses to ports, allowing them to make real-time decisions about where to send data packets.
This mechanism optimizes network traffic and significantly reduces data collisions when multiple devices attempt to communicate simultaneously. Network efficiency is drastically improved, enabling faster data transfer speeds and more reliable performance, even under heavy network loads. Switches’ efficiency becomes particularly evident in environments requiring high-speed data transmission, such as video conferencing systems and extensive data centers.
Types of Ethernet Switches
Unmanaged switches are straightforward, plug-and-play devices that are not configured. They’re perfect for small networks with low bandwidth requirements. They offer basic Ethernet functionality and are affordable and easy to set up, making them popular with non-technical users.
Managed switches offer greater control over network traffic and settings, allowing network administrators to adjust settings for enhanced security, prioritization of data types, and network performance monitoring. They contribute to the network’s overall health by enabling configuration, management, and local area network (LAN) traffic monitoring. Features such as VLANs, Quality of Service (quality of service), and SNMP support make these switches highly versatile.
Smart switches strike a balance between unmanaged and managed switches, providing some configurability while remaining relatively easy to set up and use. They are suitable for growing networks that need flexibility without the complexity of fully managed switches. They offer a middle-ground solution, providing basic management features that can be useful for small to medium-sized enterprises. Smart switches often support VLANs and essential quality of service features, offering more control than unmanaged switches. This makes them attractive for businesses looking to scale their operations without investing heavily in network management infrastructure.
Benefits of Ethernet Switching
- Efficient Data Transfer: By regulating data flow, switches minimize collisions and ensure data reaches its destination quickly. This efficiency is crucial in environments where speed and reliability are paramount, such as data centers and streaming services.
- Scalability: Ethernet switches can accommodate networks of various sizes, from small office setups to large enterprise environments. Scalability means networks can grow as needed without requiring a complete infrastructure overhaul.
- Improved Security: Managed switches often feature security options that help protect network integrity. Advanced features such as port security, access control lists, and network segmentation can mitigate risk and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Use Cases in Modern Networks
Ethernet switching is critical in transitioning from small office networks to large-scale data centers. Switches, for instance, facilitate efficient data transfer between servers and user devices at educational institutions, guaranteeing that instructors and students have dependable internet access for their assignments. This setup is vital for uninterrupted learning and effective administration.
Additionally, the rise of IoT (Internet of Things) devices has increased the demand for robust network infrastructure, further emphasizing the importance of adept switching mechanisms. Smart homes, healthcare environments, and industrial automation systems rely on efficient switches for seamless connectivity and data exchange.
In corporate environments, Ethernet switching provides the backbone for internal communications, supporting everything from email services to complex intranet applications. Enterprises can deploy managed switches to segregate traffic, ensuring mission-critical applications receive the required bandwidth and latency considerations.
Recent Advances in Ethernet Switching
Ethernet switching continues to change due to technological breakthroughs. Recent developments in switch architecture, for example, target greater energy efficiency and faster data processing capabilities. These advancements aim to meet the growing demands of digital networks while reducing operational costs.
Furthermore, integrating AI and machine learning in network management allows switches to dynamically adjust to changing network conditions, optimizing performance in real-time. This capability can be invaluable in highly variable network loads, such as cloud computing and big data analytics.
Switch capabilities include improved support for high-speed connections, with new switches offering 40 Gbps or even 100 Gbps ports. This throughput is essential for modern applications that involve large volumes of data, such as video streaming and high-frequency trading platforms.
Future Prospects and Conclusion
As networks expand and high-speed, reliable data transfer demand grows, Ethernet switching will remain pivotal. Continuous innovations in this field promise improved efficiency, scalability, and security, ensuring that it meets the future needs of diverse network environments. Adopting new technologies will necessitate Ethernet switches that can handle increased data loads and provide more intelligent and automated network management capabilities.
For businesses and consumers alike, staying ahead in the ever-evolving landscape of network technology will mean investing in robust Ethernet switches. By doing so, they can achieve higher performance, more excellent reliability, and enhanced security, ensuring their networks are ready to meet the challenges and opportunities of the future.
Stay in touch with us for more updates and alerts! Techtrand.com